Isotope labeling is a technique that can track the movement of an isotope through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. It involves replacing specific atoms with their isotopes to label the reactant. This method simplifies overlapped spectra by diluting the NMR active nuclei or separating the resonances in multiple dimensions. Isotopic labeling is a non-radioactive labeling method that allows for site-specific investigation of structures, making molecules easily detectable by mass spectrometry and NMR. It also maintains the physicochemical properties of the target molecule and is cost-effective and user-friendly. The most used isotopes for labeling are 2H (D), 13C, and 15N. Biosynthetic isotopic labeling of compounds is an alternative to pure synthetic methodologies for isotope labeling.
Quantitative proteomic analysis uses stable isotope labeling mass spectrometry to identify and quantify proteins. Methods include isotope-coded affinity tags, stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, global internal standard technology, and mass-coded abundance tagging. SILAC is a technique that uses non-radioactive isotopic labeling to detect differences in protein abundance among samples. It incorporates “heavy” labeled amino acids into proteins and uses mass spectrometry analysis to identify and quantify proteins.
Isotope labeled compounds and associated experiments play a vital role in investigating absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties of new chemical entities and metabolic flux or quantitative bioanalytical analysis. The labeled compounds typically contain some amount of native compounds, the relative amount of which can introduce systematic errors in subsequent analysis and reported results. When measured with MS, severe MS signal overlap between the labeled and un-labeled species poses a quantitative challenge even for high-resolution MS.
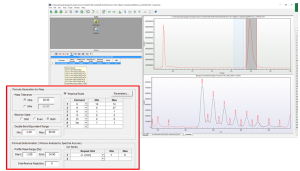
The main screen graphics shows the chromatogram (upper) and the mass spectrum (lower) of Diclofenac. The CLIPS search parameters are set to provide the best fit using all 7 possible species.
Additional resources below:
- RCMSDon Kuehl, Yongdong Wang, Peter L. Wang, Dawei Zhou
- Cold Spring Harbor LaboratoryX.Li,M.Snyder, bioRxiv
- Journal of the American Chemical SocietyCian Kingston , Michael A. Wallace, Alban J. Allentoff, Justine N. deGruyter , Jason S. Chen, Sharon X. Gong, Samuel Bonacorsi, Jr., and Phil S. Baran (see supporting information)
- WuXiAppTecD. Zhou, J. Zhao, P. L. Wang, Y. Wang, D. Kuehl
- Journal of the American Chemical SocietyErik T. Jansson, Yin-Hung Lai, Juan G. Santiago, and Richard N. Zare (see supporting information)
- CernoD.Kuehl,Y.Wang Appnote113
